Machine Learning 2.0 -Exploratory Data Analysis
In today’s post we are going to talk about Exploratory Data Analysis using the Pandas library in Azure Synapse Analytics, one of the most important steps when starting a Machine Learning project.
The Exploratory Data Analysis consists of one of the first tasks that the Data Scientist has to perform, which consists of understanding the data that comes to us and trying to identify possible patterns that may be useful to achieve the objective that is proposed to us.
Task Steps
- How many records are there? Are they too few? Are there many and we do not have enough capacity to process it?
- Are all rows complete or do we have fields with null values? In case there are too many nulls: Is the rest of the information useless? Or do we replace it with the most repeated value?
- Which data is discrete and which is continuous?
- Is the data normalized? Do we have enough samples of each kind and variety?
- If it is a supervised problem: What is the “output” column? Binary, multiclass? Is the output set balanced?
- What features are important? Which ones can we rule out? Do they follow any distribution? Is there a correlation between the characteristics we are studying?
- Are we facing a time-dependent problem?
- What are the Outliers? Are they loading errors or are they real?
EXAMPLE CASE
In order to perform all these tasks, Python provides us the Pandas library that helps us with the manipulation of the data, to be able to read, understand and transform it. Let’s see a practical example of all this using Azure Synapse Analytics:
“New York taxi drivers want to reduce their working hours but they want to make the most of their working hours, that is, they want to go to work in the time slot where the probability of receiving tips is higher.”
To do this, we take data sets from New York taxi trip records that include the following fields: pickup and drop-off dates / times, pick-up and drop-off locations, travel distances, itemized rates, rate types, rates driver’s pay and passenger counts and tip amount.
In addition, we are going to take the meteorological information to join it with that of the taxi records since we believe that it can be of vital importance since time can be a clear determining factor in the client’s decision when taking a taxi and leaving a tip.
Let’s see how to handle this data from Synapse:
import pandas as pd
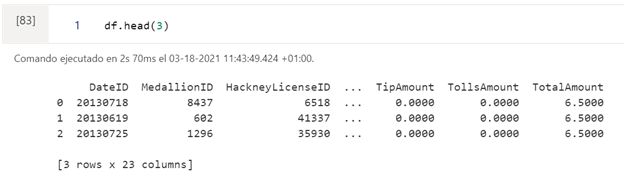
We first transform our SQL table into a Pandas dataframe and display the header.

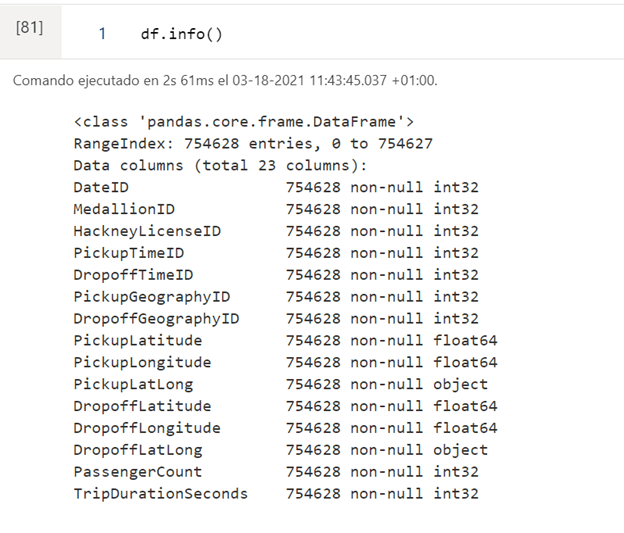
In the following output we see the names of the columns, the total of rows and the number of rows without nulls. Also the data types.
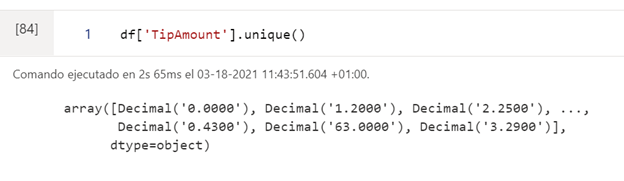
The pandas library has predefined functions, as in this case unique (), which allows us to see the possible values that a specific column (characteristic) can take:
We can also treat this type of data with SQL queries:

We have functions in the Pandas library that allow us to select certain fields of a complete date, add, sort and group.

In addition, we can define other functions that help us analyze our data:

And of course filter them:

We can also transform categorical data to numeric with the LabelEncoder() function, this is a very important function to be able to apply Machine Learning.

Which, for example, in this case is changing the attributes ‘AMRush’ by 0 and ‘Afternoon’ by 1, in this way now if we can apply a prediction algorithm, as in this case we apply logistic regression, since it only works with numeric columns.
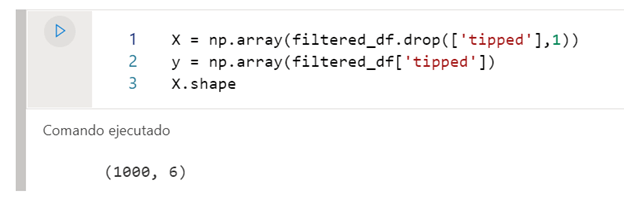
To develop the model, we will pass on the one hand the characteristics with which the model has to train, and on the other, the labels that it has to try to predict.
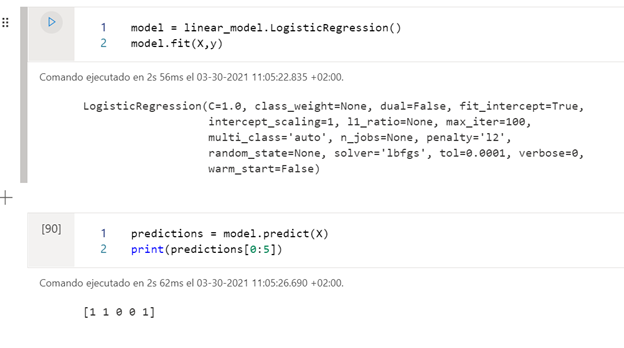
In this case, once we have trained the model, we show the predictions of whether or not they will receive a tip with the Machine Learning model that we have created. It is better before training the model to separate the entire data set into training set and test set, so as not to overfit the set.
And so far today’s post, if you are interested in the latest technologies and are learning Machine Learning, do not miss this post for beginners in Artificial Intelligence.
If you want us to help your business or company, contact us at info@aleson-itc.com or call us at +34 962 681 242

Business Intelligence Senior Consultant.

