4 Essential Cybersecurity settings in Azure AD to avoid a Cyberattack

Hello! Welcome to a new post on the Aleson ITC blog. In today’s article we will talk about some basic security settings that we should take into account within our Azure AD instances.
Identities are fundamental today within organizations, they are what give us access to our email, cloud storage, among other applications with which we carry out our work daily. That is why it becomes essential to protect these identities and prevent cybercriminals from gaining access to them.
According to the Microsoft Digital Defense Report for the year 2022, 98% of cyberattacks can be prevented by maintaining basic hygiene within our security settings. Motivated by this premise, we are going to show some basic settings that can help keep our identity environment more secure.
1. Multi-Factor Authentication
Today Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is ubiquitous, most cloud services implement it as a security mechanism to prevent unauthorized access. The MFA is a mechanism in which an additional component is added to the usual authentication flow. In addition to entering a username and password, MFA requires that we either approve a notification or enter a code that is obtained from a mobile device that we previously registered.

In Azure AD we can enable MFA for users based on the licensing we have available. If we have Microsoft 365 Business Premium, Microsoft 365 E3/E5 or Enterprise Mobility + Security E3/E5, we can deploy MFA through Conditional Access. In the case of the free version of Azure, we can enable some MFA features through Security Defaults.
2. Security Defaults
Security Defaults enables security default settings in newly created tenants, as well as being the security alternative for those tenants that are within the free tier of Azure AD. Among some of the features enabled by Security Defaults are those related to MFA.
- Require all directory users to register a device to perform MFA
- Require MFA for users with admin roles at every login
- Require MFA from users when required (Azure AD performs this assessment based on different factors)
Security Defaults is enabled by default in all tenants created after November 2019. And how do we enable Security Defaults?
Procedure to enable Security Defaults:
- Access the Azure AD administration portal.
- Go to the properties section found in the manage section of the side menu.
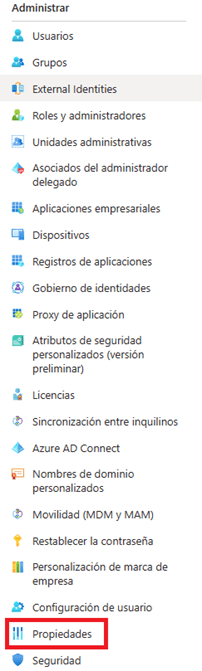
- Within this section we can see at the bottom the option “Manage Default Security Values”
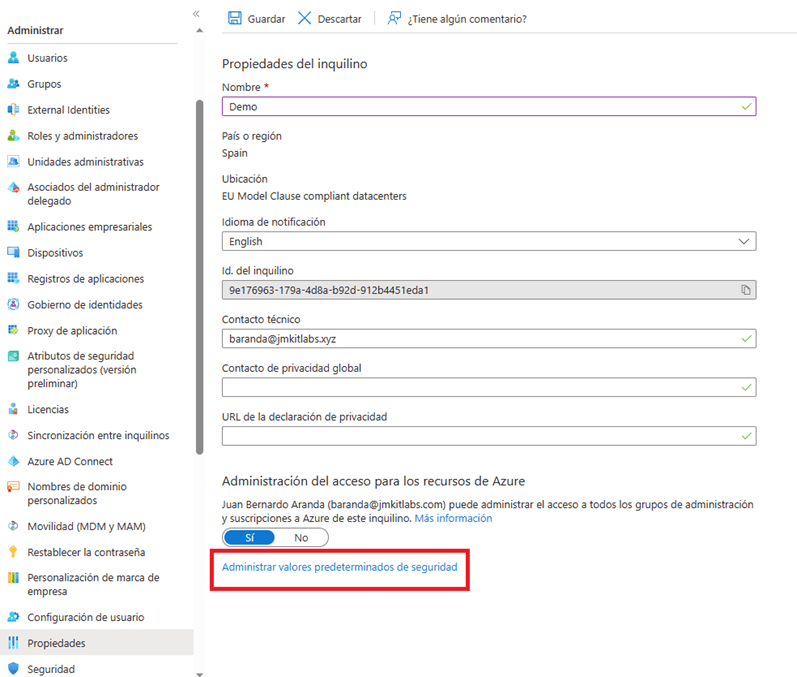
- When selecting this option we will see a side menu that shows us the status of Security Defaults, open the drop-down menu and choose “Enabled”, then press the save button that is located at the bottom of the section.

By completing this procedure we will already have the previously mentioned MFA features enabled.
3. Conditional Access
For those tenants who have an Azure AD Premium subscription, MFA can be enabled through conditional access rules, which give us greater flexibility by being able to define more specific scenarios on which to request a two-factor authentication.
Before starting with the creation of conditional access rules, we must disable Security Defaults. For this we can follow the procedure mentioned above now choosing the “Disabled” option. Once Security Defaults is disabled, the procedure to Enable MFA through Security Defaults is as follows:
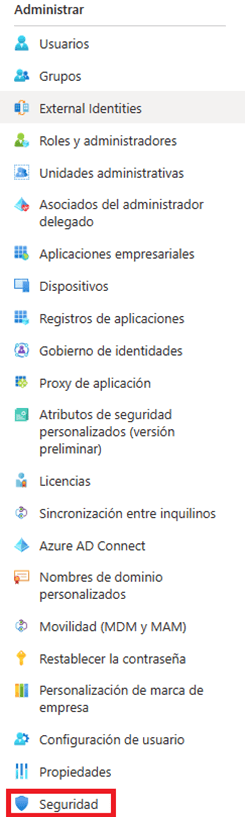
- Go to the “Security” section found in the manage section of the side menu:
- Go to the “Conditional access” section that is located at the beginning of the protect section of the side menu in the Security window.
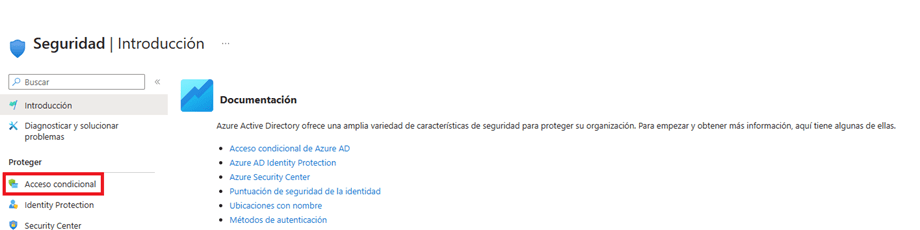
- Within the Conditional Access window, click the “Create New Policy” button.
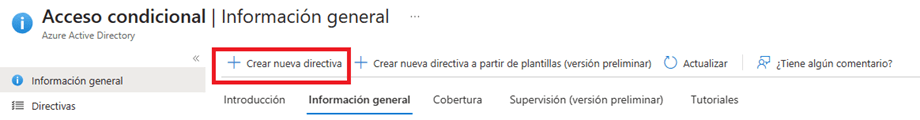
- Within the wizard for the creation of a conditional access rule we can adjust the following properties for the rule.
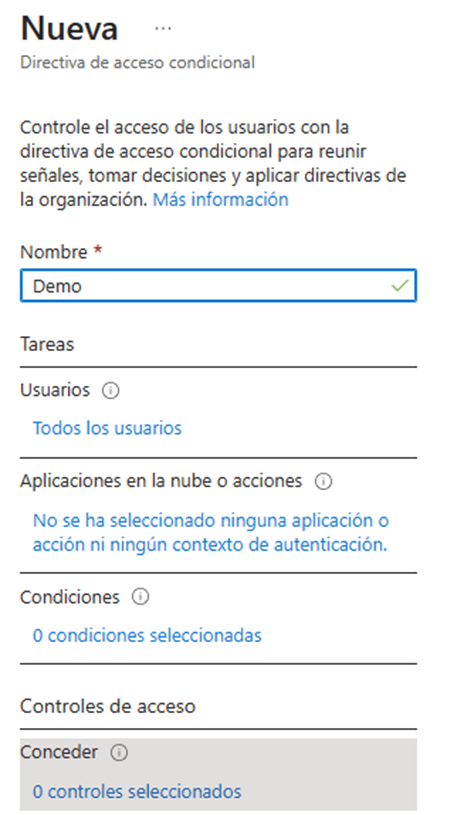
- Assigned or excluded users, here we can select specific user or groups to which the rule will be applied.
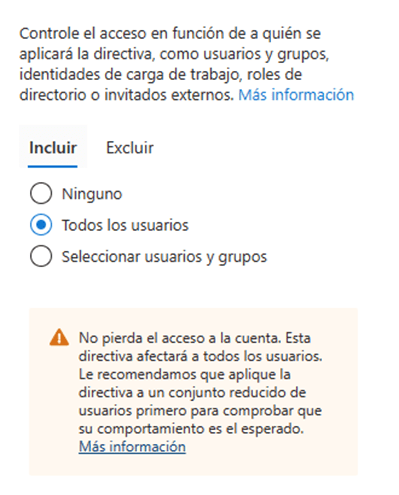
- We can choose the applications in which MFA will be requested, we can choose a certain number of them or apply to all applications in the environment.
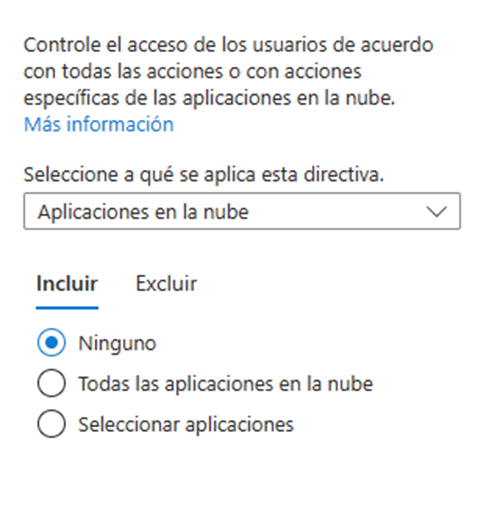
- In the conditions section we can define if the rule will be applicable for specific locations, devices or platforms. This section allows us to give the rule more granularity so that, for example, it only applies to iOS devices from a specific location.
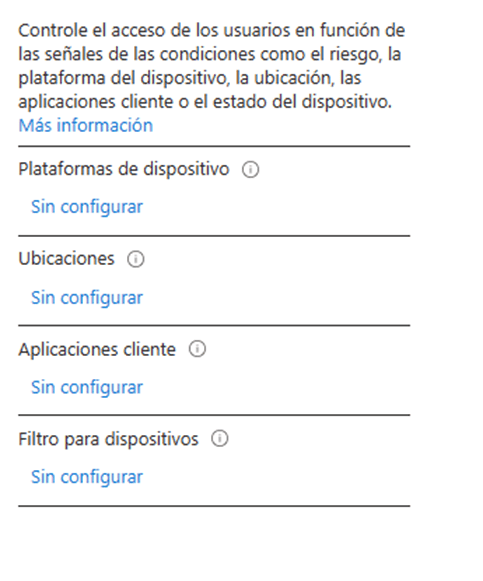
- The grant section allows us to choose the access control that should be applied to the scenario that we previously defined. In this case, we will select “Require multi-factor authentication”.
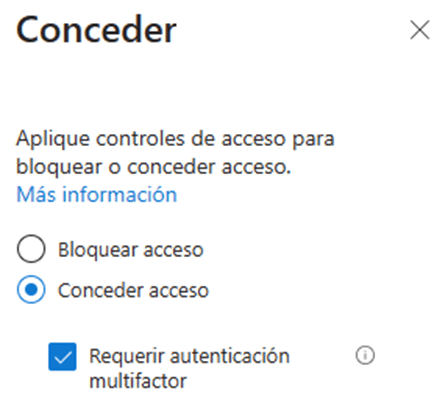
- Once all aspects of the rule have been configured, choose the “Activated” option found at the bottom of the creation wizard and press the “Create” button.
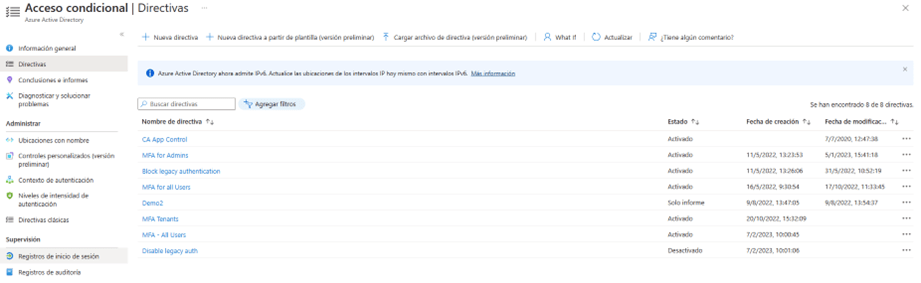
At the end of the procedure we will have created our conditional access rule that implements MFA. Said rule can be consulted in the “Directives” section within the Conditional Access section.
4. Users Configuration
By default, all users within an Azure AD tenant are allowed to perform actions such as register new applications within the environment, grant permissions to applications, create new tenants, groups, or send invitations to third parties to enter the environment to the organization’s Azure AD . The misuse of these functionalities can generate significant security breaches that violate the integrity of identities. The following steps show how to prevent non-administrator users from modifying environment properties.
- Access the Azure Active Directory Administration portal.
- Go to the “User Settings” section found in the “Manage” section of the side menu.
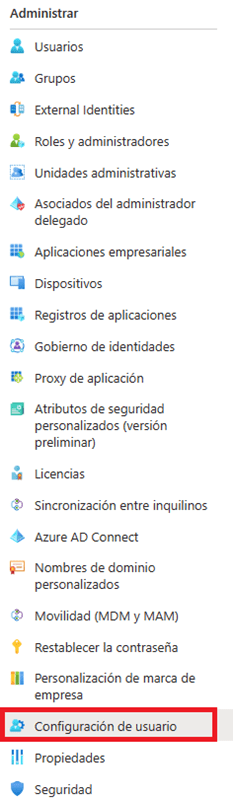
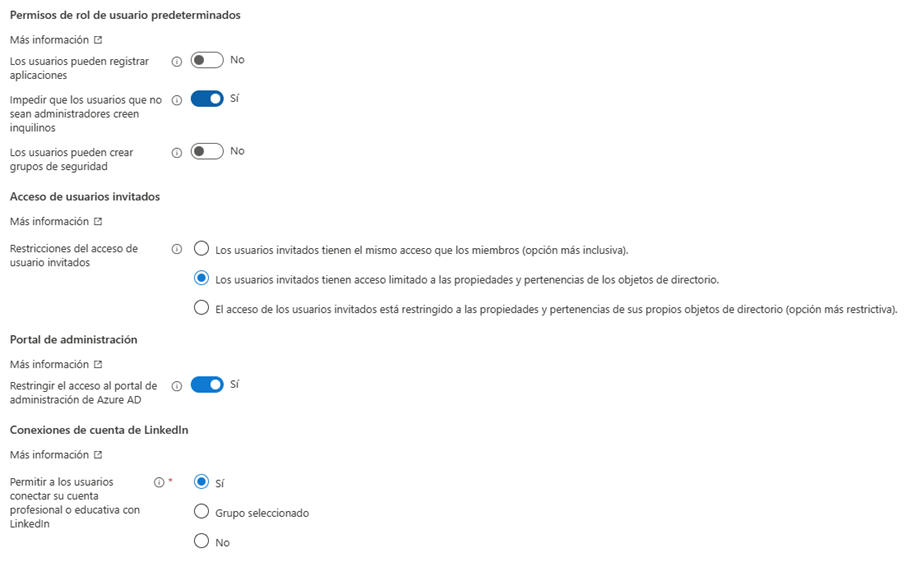
- Within the User Configuration window we modify the values as shown in the screenshot.
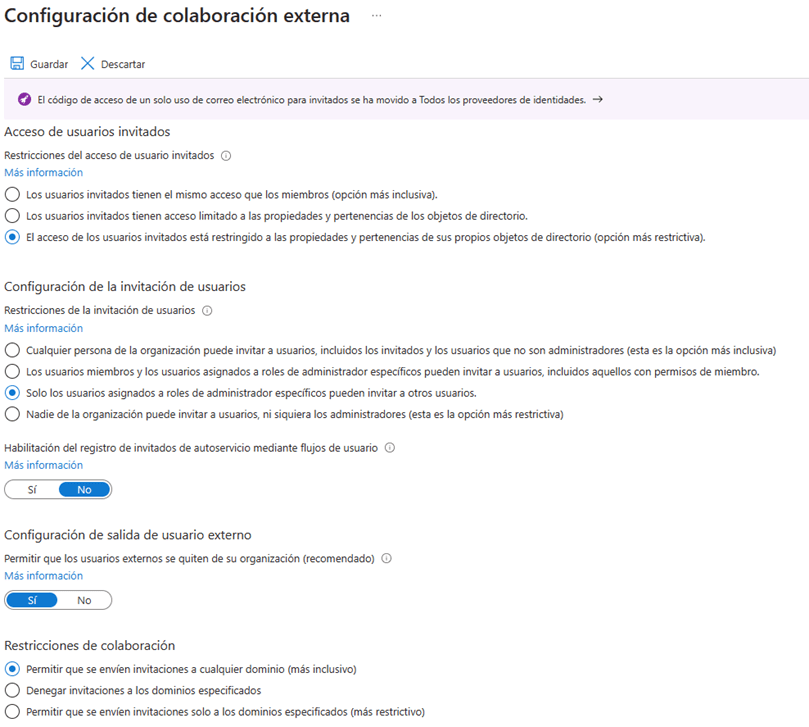
- Within the User Configuration window, click on the option “Administration of external collaboration configuration”.
- Within the “External collaboration configuration” window, modify the values as follows.
After carrying out these actions, we will have increased the security of our identities a little more, although it is important to note that maintaining the security of our environment is an ongoing task that we must proactively follow up on when new threats appear.
And here is today’s article, I hope this entry will be of help to you within the security strategy in your organization.
And if you liked it, we recommend you go through our latest articles:
Incremental Refresh & Real Time with Direct Query in Power BI
6 Fundamental Steps for Efficient and Successful Project Management
How to Configure pgbackrest in PostgreSQL to back up to Azure
If you need help with any deployment within the Microsoft 365 security platform, at Aleson ITC we can help you.

Security Engineer.

